- 23 Aug, 2023
- read
- Karolinehc
Categories: Programming Languages Data Analysis
Tags: SQL Database Queries SELECT Filtering JOIN Data Analytics T-SQL
The content presented in this article is intended solely for academic purposes. The opinions expressed are based on my personal understanding and research. It’s important to note that the field of big data and the programming languages discussed, such as Python, R, Power BI, Tableau, and SQL, are dynamic and constantly evolving. This article aims to foster learning, exploration, and discussion within the field rather than provide definitive answers. Reader discretion is advised.
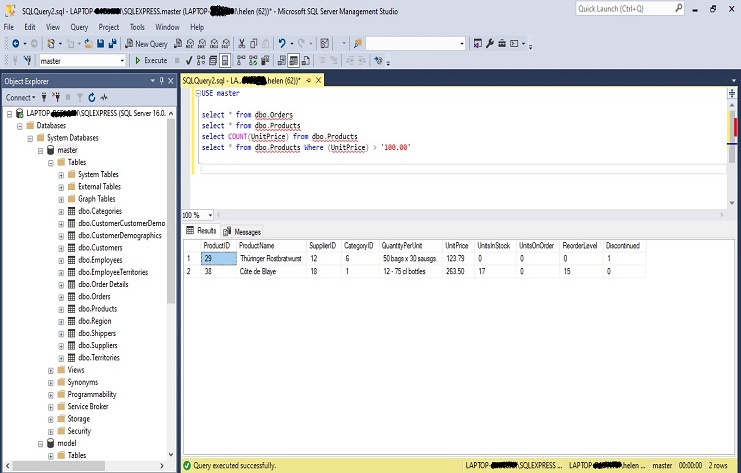
USE master: This statement is used to change the database context to the “master” database
select * from dbo.Products: This part of the query selects all columns from the table named “Products” in the current database.
Notice
USE master select * from dbo.Products
SQL
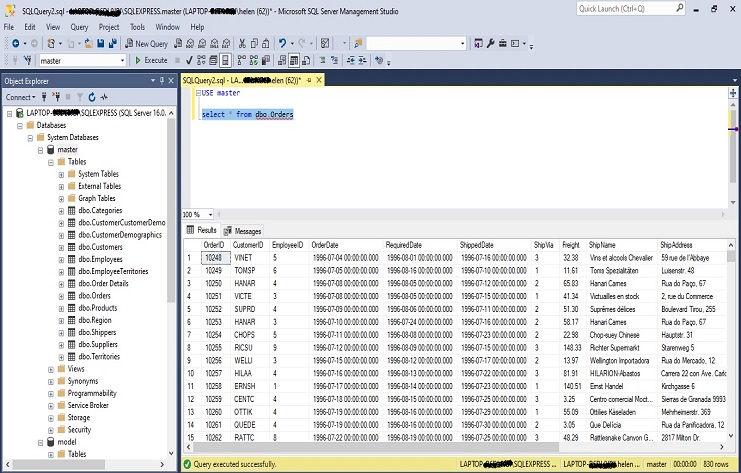
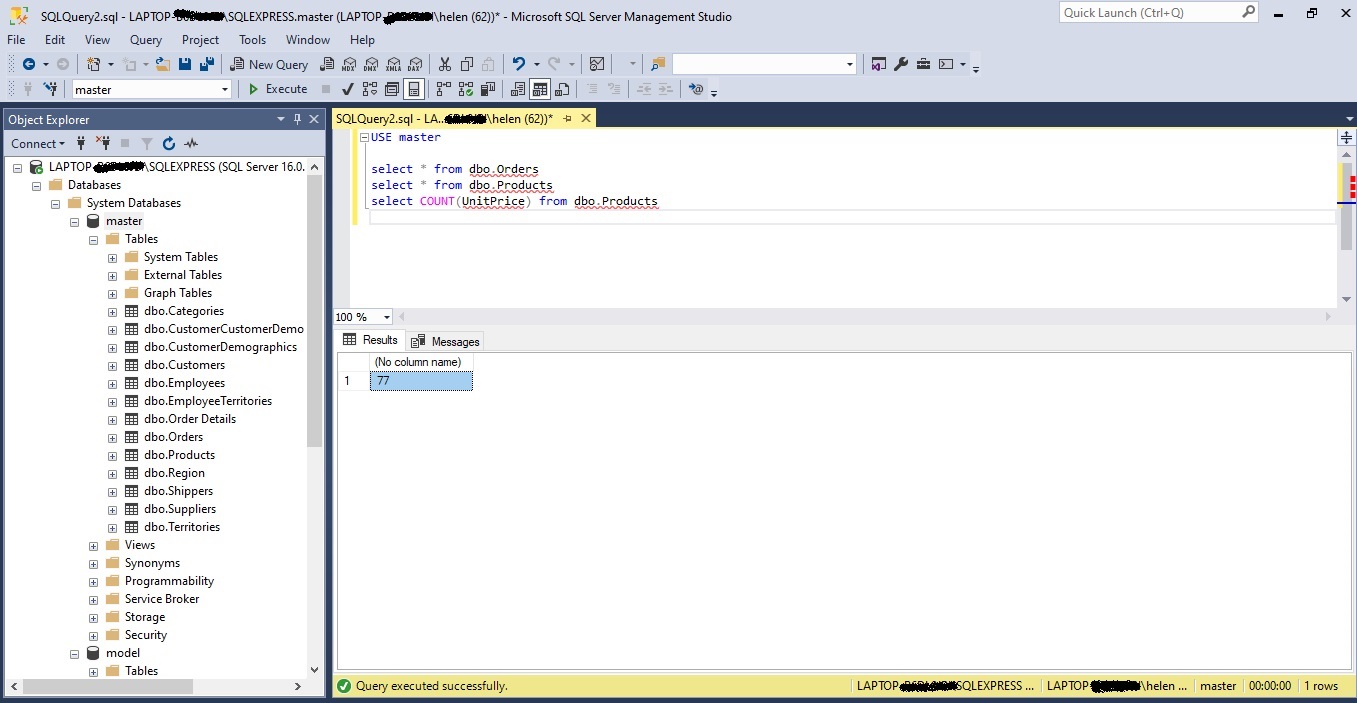
to count the total number of rows in the “dbo.Products” table, you should use the COUNT(UnitPrice) function like this:
Notice
SELECT COUNT(UnitPrice) FROM dbo.Products;
SQL
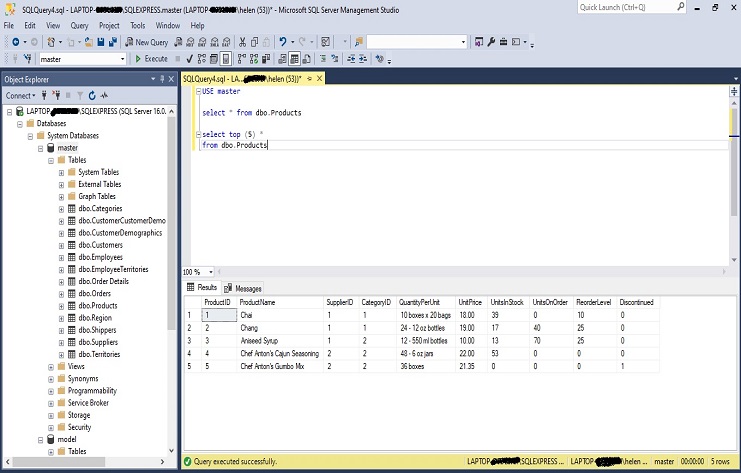
It will retrieve the top 5 rows from the “dbo.Products” table. The TOP clause is used to limit the number of rows returned in the result set. In this case, it specifies that you want to retrieve the first 5 rows based on the default order of the table (usually the order in which the rows were inserted).
Notice
SELECT TOP (5) * FROM dbo.Products;
SQL
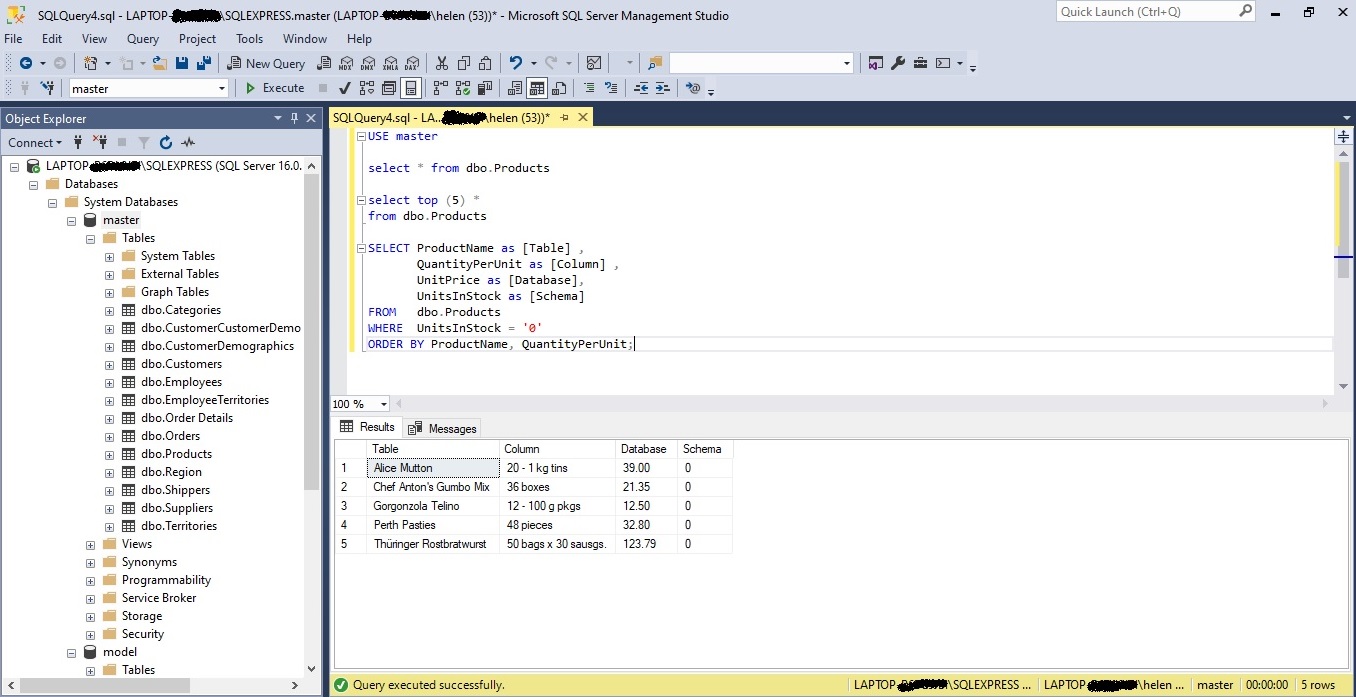
Retrieving specific columns from the “dbo.Products” table, filtering the rows where the “UnitsInStock” column has a value of ‘0’, and ordering the results by “ProductName” and “QuantityPerUnit
Notice
SELECT ProductName as [Table], QuantityPerUnit as [Column], UnitPrice as [Database], UnitsInStock as [Schema] FROM dbo.Products WHERE UnitsInStock = ‘0’ ORDER BY ProductName, QuantityPerUnit;
SQL
Alter database: This statement is used to modify database-level settings and properties.
Select * from dbo.Products: This is a query that retrieves all columns from the “dbo.Products” table. It’s not related to the “Alter database” statement
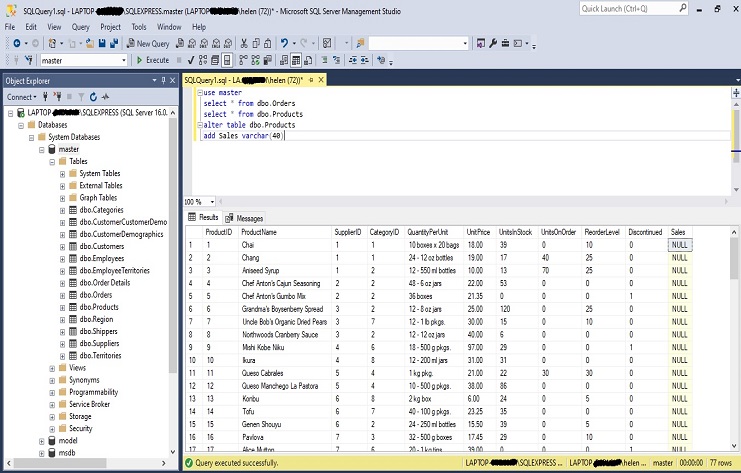
Alter table dbo.Products add Sales varchar(40): This statement is trying to alter the “dbo.Products” table by adding a new column called “Sales” with a varchar data type that can hold up to 40 characters.
Notice
Alter database select * from dbo.Products alter table dbo.Products add Sales varchar(40)
SQL
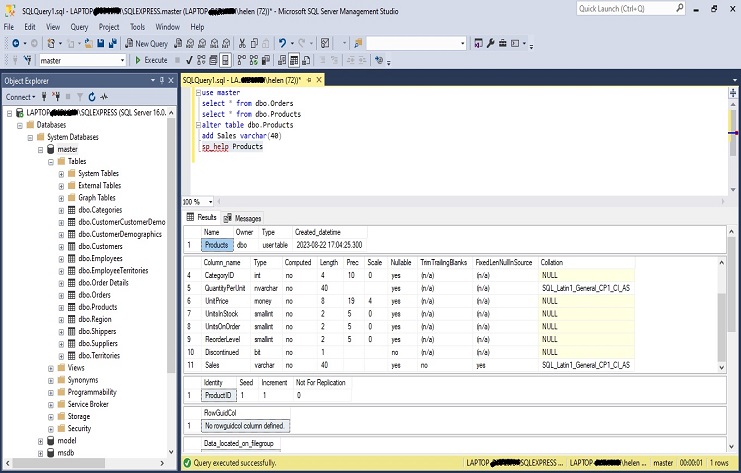
The sp_help command is used to retrieve information about a database object, such as a table. In this case, we want to retrieve information about the “Products” table. Here’s how we would use the sp_help command:
Notice
sp_help ‘dbo.Products’;
SQL
This should return the rows where the “UnitPrice” is greater than 100.
Notice
Select * from dbo.Products Where (UnitPrice) > ‘100’
SQL